Hidden Pairs
If two candidates can be found in only the same two Cells of a region (Row, Column or Square), then one of these candidates is the solution for one of these Cells and the other candidate is the solution for the other Cell.
Hence all other candidates can be deleted from these two Cells.
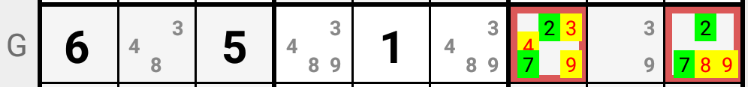
In the example above candidates 2 and 7 are only allowed in Cells G7 and G9 of Row "G". If candidate 2 is the solution in G7, then candidate 7 must be the solution in G9. Conversely, if candidate 2 is the solution in G9, then candidate 7 must be the solution in G7. Hence Cells G7 and G9 must have 2 or 7 as solution; all other candidates can be deleted from G7 and G9.
You can practice this strategy by installing the free SudokuCoach application on your Android™ device.
